


Greg Perr y
C++ By Example
© 1992 by Qu e
All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. No part of this book may be used or reproduced, in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without prior written permission of the publisher except in the case of brief quotations embodied in critical articles and reviews. Making copies of any part of this book for any purpose other than your own personal use is a violation of United States copyright laws. For information, address Que, 11711 N. College Ave., Carmel, IN 46032.
Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 92-64353 ISBN: 1-56529-038-0
This book is sold as is, without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, respecting the contents of this book, including but not limited to implied warranties for the book’s quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Neither Que Corporation nor its dealers or distributors shall be liable to the purchaser or any other person or entity with respect to any liability, loss, or damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by this book.
96 95 94 93 92 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Interpretation of the printing code: the rightmost double-digit number is the year of the book’s printing; the rightmost single-digit number, the number of the book’s printing. For example, a printing code of 92-1 shows that the first printing of the book occurred in 1992.
 Publisher
Publisher
Lloyd Short
Publishing Manager
Joseph Wikert
Development Editor
Stacy Hiquet
Production Editor
Kezia Endsley
Copy Editor
Bryan Gambrel
Technical Editor
Tim Moore
Editorial Assistants Rosemarie Graham Melissa Keegan
Book Design Scott Cook Michele Laseau
Production Analyst
Mary Beth Wakefield
Cover Design
Jean Bisesi
Indexer
Johnna VanHoose
Production
Caroline Roop (Book Shepherd) Jeff Baker, Paula Carroll, Michelle Cleary, Brook Farling, Kate Godfrey, Bob LaRoche, Laurie Lee, Jay Lesandrini, Cindy L. Phipps, Linda Seifert, Phil Worthington
Composed in Palatino and MCPdigital typefaces by Prentice Hall Computer Publishing. Screen reproductions in this book were created by means of the program Collage Plus from Inner Media, Inc., Hollis, NH.
Dr. Rick Burgess, you shaped my life. Good or bad, I’m what I am thanks to your help. I appreciate the many hours we’ve shared together.
G.M.P.
Greg Perry has been a programmer and trainer for the past 14 years. He received his first degree in computer science, then he received a Masters degree in corporate finance. He currently is a professor of computer science at Tulsa Junior College, as well as a computer consultant and a lecturer. Greg Perry is the author of 11 other computer books, including QBASIC By Example and C By Example. In addition, he has published articles in several publications, including PC World, Data Training, and Inside First Publisher. He has attended computer conferences and trade shows in several countries, and is fluent in nine computer languages.
Acknowledgments
Much thanks to Stacy Hiquet and Joseph Wikert at Prentice Hall (Que) for trusting me completely with the direction and style of this book. The rest of my editors: Kezia Endsley, Bryan Gambrel, and the Technical Editor, Tim Moore, kept me on track so the readers can have an accurate and readable text.
The Tulsa Junior College administration continues to be sup- portive of my writing. More importantly, Diane Moore, head of our Business Services Division, Tony Hirad, and Elaine Harris, are friends who make teaching a joy and not a job.
As always, my beautiful bride Jayne, and my parents Glen and Bettye Perry, are my closest daily companions. It is for them I work.
Trademark Acknowledgment s
Que Corporation has made every attempt to supply trademark information about company names, products, and services men- tioned in this book. Trademarks indicated below were derived from various sources. Que Corporation cannot attest to the accuracy of this information.
AT&T is a registered trademark of American Telephone & Telegraph Company.
FORTRAN and COBOL are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation (IBM).
Turbo BASIC is a registered trademark of Borland International, Inc.
Turbo C is a registered trademark of Borland International, Inc. Microsoft QuickC and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
ANSI is a registered trademark of American National Standards Institute.
-
Introduction to C+ +
-
Welcome to C++ 11
-
What Is a Program? 35
-
Your First C++ Program 51
-
Variables and Literals 69
-
Character Arrays and Strings 99
-
Preprocessor Directives 113
-
Simple Input/ Output 133
-
-
Using C++ Operator s
-
Using C++ Math Operators and Precedence 163
-
Relational Operators 185
-
Logical Operators 207
-
Additional C++ Operators 221
C++ Construct s
-
The while Loop 245
-
The for Loop 273
-
Other Loop Options 295
-
The switch and goto Statements 311
-
Writing C++ Functions 331
Variable Scope and Modula r Programming
-
Variable Scope 353
-
Passing Values 379
-
Function Return Values and Prototypes 397
-
Default Arguments and Function Overloading 415
Character Inp ut/ Output an d String Function s
-
Device and Character Input/ Output 431
-
Character, String, and Numeric Functions 449
Arrays and Pointer s
-
Introducing Arrays 473
-
Array Processing 493
-
Multidimensional Arrays 519
-
Pointers 541
-
Pointers and Arrays 557
Structures and File Input/Outpu t
-
Structures 583
-
Arrays of Structures 605
-
Sequential Files 625
-
Random-Access Files 645
-
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming 661
References
-
Memory Addressing, Binary, and Hexadecimal Review 679
-
Answers to Review Questions 701
-
ASCII Table 719
-
C++ Precedence Table 729
-
Keyword and Function Reference 733
-
The Mailing List Application 737
Glossary 747
Index 761
Introduction 1
Who Should Use This Book 1
The Book’s Philosophy 2
Overview of This Book 2
Conventions Used in This Book 5
Index to the Icons 5
Margin Graphics (Book Diagrams) 6
Companion Disk Offer 8
-
Introduction to C+ +
- Welcome to C+ + 11
What C++ Can Do for You 12
The Background of C++ 15
C++ Compared with Other Languages 16
C++ and Microcomputers 17
An Overview of Your Computer 19
Hardware 19
Software 29
Review Questions 33
Summary 34
- What Is a Program ? 35
Computer Programs 36
Program Design 38
Using a Program Editor 40
Using a C++ Compiler 42
Running a Sample Program 44
Handling Errors 46
Review Questions 48
Summary 49
Contents♦
- Your First C++ Progra m 51
The Format of a C++ Program 53
Braces and main() 56
Explaining the Sample Program 60
- Variables and Literal s 69
Assigning Values to Variables 80
Assigning Character Literals 89
- Character Arrays and String s 99
Character Arrays Versus Strings 103
- Preprocessor Directive s 113
Understanding Preprocessor Directives 114
The #include Directive 115
The #define Directive 120
EXAMPLE
Review Questions 128
Review Exercises 130
Summary 130
- Simple Input/Outpu t 133
The cout Operator 134
Printing Strings 134
The cin Operator 144
printf() and scanf() 149
The printf() Function 149
Conversion Characters 151
The scanf() Function 154
Review Questions 157
Review Exercises 158
Summary 159
Using C++ Operator s
- Using C++ Math Operator s
and Precedenc e 163
C++’s Primary Math Operators 164
The Unary Operators 165
Division and Modulus 167
The Order of Precedence 168
Using Parentheses 170
The Assignment Statements 174
Multiple Assignments 175
Compound Assignments 176
Mixing Data Types in Calculations 178
Type Casting 179
Review Questions 182
Review Exercises 183
Summary 184
- Relational Operator s 185
Defining Relational Operators 186
The if Statement 189
The else Statement 199
Contents♦
Review Questions 203
Review Exercises 204
Summary 205
- Logical Operator s 207
Defining Logical Operators 207
Logical Operators and Their Uses 209
C++’s Logical Efficiency 211
Logical Operators and Their Precedence 216
Review Questions 217
Review Exercises 218
Summary 219
- Additional C++ Operator s 221
The Conditional Operator 222
The Increment and Decrement Operators 225
The sizeof Operator 230
The Comma Operator 232
Bitwise Operators 234
Bitwise Logical Operators 235
Review Questions 242
Review Exercises 243
Summary 243
C++ Construct s
- The while Loop 245
The while Statement 246
The Concept of Loops 247
The do-while Loop 252
The if Loop Versus the while Loop 255
The exit() Function and break Statement 256
Counters and Totals 260
Producing Totals 265
Review Questions 268
Review Exercises 269
Summary 270
EXAMPLE
- The for Loop 273
The for Statement 274
The Concept of for Loops 274
Nested for Loops 286
Review Questions 292
Review Exercises 293
Summary 293
- Other Loop Option s 295
Timing Loops 296
The break and for Statements 298
The continue Statement 303
Review Questions 308
Review Exercises 308
Summary 309
- The switch and goto Statements 311
The switch Statement 312
The goto Statement 321
Review Questions 327
Review Exercises 328
Summary 328
- Writing C++ Function s 331
Function Basics 332
Breaking Down Problems 333
More Function Basics 335
Calling and Returning Functions 337
Review Questions 349
Summary 350
Variable Scope and Modular Programmin g
- Variable Scop e 353
Global Versus Local Variables 354
Defining Variable Scope 355
Use Global Variables Sparingly 362
The Need for Passing Variables 363
Automatic Versus Static Variables 369
Contents♦
Three Issues of Parameter Passing 374
Review Questions 375
Review Exercises 375
Summary 377
- Passing Value s 379
Passing by Value (by Copy) 379
Passing by Address (by Reference) 385
Variable Addresses 385
Sample Program 386
Passing Nonarrays by Address 391
Review Questions 394
Review Exercises 395
Summary 396
- Function Return Values and Prototype s 397
Function Return Values 398
Function Prototypes 405
Prototype for Safety 407
Prototype All Functions 407
Review Questions 412
Review Exercises 412
Summary 413
- Default Argument s
and Function Overloadin g 415
Default Argument Lists 416
Multiple Default Arguments 417
Overloaded Functions 420
Review Questions 426
Review Exercises 426
Summary 427
Character Inp ut/Output and String Function s
- Device and Character Input/Outpu t 431
Stream and Character I/ O 432
Standard Devices 434
Redirecting Devices from MS-DOS 435
EXAMPLE
Printing Formatted Output to the Printer 436
Character I/ O Functions 437
The get() and put() Functions 438
The getch() and putch() Functions 444
Review Questions 446
Review Exercises 447
Summary 448
- Character, String ,
and Numeric Function s 449
Character Functions 450
Character Testing Functions 450
Alphabetic and Digital Testing 450
Special Character-Testing Functions 453
Character Conversion Functions 453
String Functions 455
Useful String Functions 456
String I/ O Functions 456
Converting Strings to Numbers 460
Numeric Functions 461
Useful Mathematical Functions 461
Trigonometric Functions 464
Logarithmic Functions 465
Random-Number Processing 465
Review Questions 467
Review Exercises 468
Summary 469
Arrays and Pointer s
- Introducing Array s 473
Array Basics 474
Initializing Arrays 479
Initializing Elements at Declaration Time 479
Initializing Elements in the Program 486
Review Questions 491
Review Exercises 491
Summary 492
Contents♦
- Array Processin g 493
Searching Arrays 494
Searching for Values 496
Sorting Arrays 501
Advanced Referencing of Arrays 508
Review Questions 515
Review Exercises 516
Summary 517
- Multidimensional Array s 519
Multidimensional Array Basics 520
Reserving Multidimensional Arrays 522
Mapping Arrays to Memory 524
Defining Multidimensional Arrays 526
Tables and for Loops 530
Review Questions 537
Review Exercises 538
Summary 538
- Pointers 541
Introduction to Pointer Variables 542
Declaring Pointers 543
Assigning Values to Pointers 545
Pointers and Parameters 546
Arrays of Pointers 551
Review Questions 553
Summary 555
- Pointers and Array s 557
Array Names as Pointers 558
Pointer Advantages 560
Using Character Pointers 563
Pointer Arithmetic 568
Arrays of Strings 574
Review Questions 578
Review Exercises 579
Summary 580
EXAMPLE
Structures and File Input/Outpu t
- Structures 583
Introduction to Structures 584
Defining Structures 587
Initializing Structure Data 591
Nested Structures 600
Review Questions 603
Review Exercises 604
Summary 604
- Arrays of Structure s 605
Declaring Arrays of Structures 606
Arrays as Members 615
Review Questions 623
Review Exercises 624
Summary 624
- Sequential File s 625
Why Use a Disk? 626
Types of Disk File Access 627
Sequential File Concepts 628
Opening and Closing Files 629
Writing to a File 635
Writing to a Printer 637
Adding to a File 638
Reading from a File 639
Review Questions 642
Review Exercises 643
Summary 644
- Random-Access File s 645
Random File Records 646
Opening Random-Access Files 647
The seekg() Function 649
Other Helpful I/ O Functions 656
Review Questions 658
Review Exercises 658
Summary 659
Contents♦
- Introduction to Object-Oriente d
Programming 661
What Is a Class? 662
Data Members 662
Member Functions 662
Default Member Arguments 670
Class Member Visibility 674
Review Questions 676
Review Exercise 676
Summary 676
References
- Memory Addressing, Binary ,
and Hexadecimal Revie w 679
Computer Memory 680
Memory and Disk Measurements 680
Memory Addresses 681
Bits and Bytes 682
The Order of Bits 686
Binary Numbers 686
Binary Arithmetic 690
Binary Negative Numbers 692
Hexadecimal Numbers 695
Why Learn Hexadecimal? 697
How Binary and Addressing Relate to C++ 698
-
Answers to Review Question s 701
-
ASCII Tabl e 719
-
C++ Precedence Tabl e 729
-
Keyword and Function Referenc e 733
stdio.h 734
ctype.h 734
string.h 735
math.h 735
stdlib.h 735
EXAMPLE
- The Mailing List Applicatio n 737
Glossary 747
Index 761

Introduction
Every day, more and more people learn and use the C++ program- ming language. I have taught C to thousands of students in my life. I see many of those students now moving to C++ in their school work or career. The C++ language is becoming an industry-accepted standard programming language, using the solid foundation of C to gain a foothold. C++ is simply a better C than C.
C++ By Example is one of several books in Que’s new line of By Example series. The philosophy of these books is simple: The best way to teach computer programming concepts is with multiple examples. Command descriptions, format syntax, and language references are not enough to teach a newcomer a programming language. Only by looking at numerous examples and by running sample programs can programming students get more than just a “feel” for the language.
Who Should Use This Boo k
This book teaches at three levels: beginning, intermediate, and advanced. Text and numerous examples are aimed at each level. If you are new to C++, and even if you are new to computers, this book attempts to put you at ease and gradually build your C++ program- ming skills. If you are an expert at C++, this book provides a few extras for you along the way.
Introduction ♦
The Book’s Philosoph y
This book focuses on programming correctly in C++ by teaching structured programming techniques and proper program design. Emphasis is always placed on a program’s readability rather than “tricks of the trade” code examples. In this changing world, pro- grams should be clear, properly structured, and well-documented, and this book does not waver from the importance of this philos- ophy.
This book teaches you C++ using a holistic approach. In addi- tion to learning the mechanics of the language, you learn tips and warnings, how to use C++ for different types of applications, and a little of the history and interesting asides about the computing industry.
Many other books build single applications, adding to them a little at a time with each chapter. The chapters of this book are stand- alone chapters, and show you complete programs that fully demon- strate the commands discussed in the chapter. There is a program for every level of reader, from beginning to advanced.
This book contains almost 200 sample program listings. These programs show ways that you can use C++ for personal finance, school and business record keeping, math and science, and general- purpose applications that almost everybody with a computer can use. This wide variety of programs show you that C++ is a very powerful language that is easy to learn and use.
Appendix F, “The Mailing List Application,” is a complete application—much longer than any of the other programs in the book—that brings together your entire working knowledge of C++. The application is a computerized mailing-list manager. Through- out the chapters that come before the program, you learn how each command in the program works. You can modify the program to better suit your own needs. (The comments in the program suggest changes you can make.)
Overview of This Boo k
This book is divided into eight parts. Part I introduces you to the C++ environment, as well as introductory programming con- cepts. Starting with Part II, the book presents the C++ programming
EXAMPLE
language commands and built-in functions. After mastering the language, you can use the book as a handy reference. When you need help with a specific C++ programming problem, turn to the appropriate area that describes that part of the language to see numerous examples of code.
To get an idea of the book’s layout, read the following descrip- tion of each section of the book:
Part I: Introduction to C+ +
This section explains what C++ is by describing a brief history of the C++ programming language and presenting an overview of C++’s advantages over other languages. This part describes your computer’s hardware, how you develop your C++ programs, and the steps you follow to enter and run programs. You begin to write C++ programs in Chapter 3.
Part II: Using C++ Operator s
This section teaches the entire set of C++ operators. The rich assortment of operators (more than any other programming lan- guage except APL) makes up for the fact that the C++ programming language is very small. The operators and their order of precedence are more important to C++ than most programming languages.
Part III: C++ Construct s
C++ data processing is most powerful due to the looping, comparison, and selection constructs that C++ offers. This part shows you how to write programs flowing with control computa- tions that produce accurate and readable code.
Part IV: Variable Scope an d Modular Programmin g
To support true structured programming techniques, C++ must allow for local and global variables, as well as offer several
Introduction ♦
ways to pass and return variables between functions. C++ is a very strong structured language that attempts, if the programmer is willing to “listen to the language,” to protect local variables by making them visible only to the parts of the program that need them.
Part V: Character Inpu t/ Output an d String Function s
C++ contains no commands that perform input or output. To make up for this apparent oversight, C++ compiler writers supply several useful input and output functions. By separating input and output functions from the language, C++ achieves better portability between computers; if your program runs on one computer, it will work on any other.
This part also describes several of the other built-in math, character, and string functions available with C++. These functions keep you from having to write your own routines to perform common tasks.
Part VI: Arrays and Pointer s
C++ offers single and multidimensional arrays that hold mul- tiple occurrences of repeating data, but that do not require much effort on your part to process.
Unlike many other programming languages, C++ also uses pointer variables a great deal. Pointer variables and arrays work together to give you flexible data storage that allow for easy sorting and searching of data.
Part VII: Structures and Fil e Input/Output
Variables, arrays, and pointers are not enough to hold the types of data that your programs require. Structures allow for more powerful grouping of many different kinds of data into manageable units.
Your computer would be too limiting if you could not store data to the disk and retrieve that data back in your programs. Disk
EXAMPLE
files are required by most “real world” applications. This section describes how C++ processes sequential and random-access files and teaches the fundamental principles needed to effectively save data to the disk. The last chapter in this section introduces object- oriented programming and its use of classes.
Part VIII: Reference s
This final section of the book includes a reference guide to the ASCII table, the C++ precedence table, and to keywords and func- tions in C++. Also in this section are the mailing list application and the answers to the review questions.
Conventions Used in Thi s Book
The following typographic conventions are used in this book:
- Code lines, variables, and any text you see on-screen are in
monospace .
-
Placeholders on format lines are in i t ali c monospace .
-
Filenames are in regular text, all uppercase (CCDOUB.CPP).
-
Optional parameters on format lines are enclosed in flat brackets
([ ] ). You do not type the brackets when you include these parameters.
-
New terms, which are also found in the glossary, are in italic.
Index to the Icon s
The following icons appear throughout this book:
 Level 1 difficulty
Level 1 difficulty
Introduction ♦
 Level
2 difficulty
Level
2 difficulty
Level 3 difficulty
 Tip
Tip
 Note
Note
Caution
Pseudocode
The pseudocode icon appears beside pseudocode, which is typeset in italic immediately before the program. The pseudocode consists of one or more sentences indicating what the program instructions are doing, in English. Pseudocode appears before se- lected programs.
Margin Graphics (Book Diagrams )
To help your understanding of C++ further, this book includes numerous margin graphics. These margin graphics are similar to flowcharts you have seen before. Both use standard symbols to represent program logic. If you have heard of the adage “A picture is worth a thousand words,” you will understand why it is easier to look at the margin graphics and grasp the overall logic before dissecting programs line-by-line.
EXAMPLE
Throughout this book, these margin graphics are used in two places. Some graphics appear when a new command is introduced, to explain how the command operates. Others appear when new commands appear in sample programs for the first time.
The margin graphics do not provide complete, detailed expla- nations of every statement in each program. They are simple instruc- tions and provide an overview of the new statements in question. The symbols used in the margin graphics, along with descriptions of them, follow:
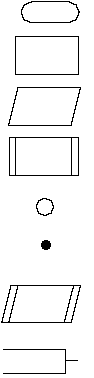 Terminal
symbol
Terminal
symbol
( { , } , Ret ur n. . . )
Assignment staement (t ot al =
t ot al + newval ue; ct r = ct r = 1; . . . )
Input/output
( scanf , pr i nt f... )
Calling a function
Small circle; loop begin
Large dot; begining and end of I F- THEN, I F- THEN- ELSE ,
and Swi t ch
Input/output of arrays; assumes implied FOR loop(s) needed to deal with array I/O
Comment bracket; used for added info, such as name of a function
Introduction ♦
The margin graphics, the program listings, the program com- ments, and the program descriptions in the book provide many vehicles for learning the C++ language!
Companion Disk Offe r
If you’d like to save yourself hours of tedious typing, use the order form in the back of this book to order the companion disk for C++ By Example. This disk contains the source code for all complete programs and sample code in this book, as well as the mailing-list application that appears in Appendix F. Additionally, the answers to many of the review exercises are included on the disk.

Part I
Introduction to C++
 Welcome to C+
+
Welcome to C+
+
C++ is a recent addition to the long list of programming languages now available. Experts predict that C++ will become one of the most widely used programming languages within two to three years. Scan your local computer bookstore’s shelves and you will see that C++ is taking the programming world by storm. More and more companies are offering C++ compilers. In the world of PCs, both Borland and Microsoft, two of the leading names of PC software, offer full-featured C++ compilers.
Although the C++ language is fairly new, having become popular within the last three years, the designers of C++ compilers are perfecting this efficient, standardized language that should soon be compatible with almost every computer in the world. Whether you are a beginning, an intermediate, or an expert programmer, C++ has the programming tools you need to make your computer do just what you want it to do. This chapter introduces you to C++, briefly describes its history, compares C++ to its predecessor C, shows you the advantages of C++, and concludes by introducing you to hard- ware and software concepts.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
What C++ Can Do for Yo u
C++ is currently Imagine a language that makes your computer perform to your
defined by American Telephone & Telegraph, Incorporated, to achieve conformity between versions
of C++.

C++ is called a “better C than C.”
personal specifications! Maybe you have looked for a program that keeps track of your household budget—exactly as you prefer—but haven’t found one. Perhaps you want to track the records of a small (or large) business with your computer, but you haven’t found a program that prints reports exactly as you’d like them. Possibly you have thought of a new and innovative use for a computer and you would like to implement your idea. C++ gives you the power to develop all these uses for your computer.
If your computer could understand English, you would not have to learn a programming language. But because it does not understand English, you must learn to write instructions in a language your computer recognizes. C++ is a powerful program- ming language. Several companies have written different versions of C++, but almost all C++ languages available today conform to the AT&T standard. AT&T-compatible means the C++ language in ques- tion conforms to the standard defined by the company that invented the language, namely, American Telephone & Telegraph, Incorpo- rated. AT&T realizes that C++ is still new and has not fully matured. The good people there just completed the AT&T C++ 3.0 standard to which software companies can conform. By developing a uniform C++ language, AT&T helps ensure that programs you write today will most likely be compatible with the C++ compilers of tomorrow.
Companies do not have to follow the AT&T C++ 3.0 standard. Many do, but add their own extensions and create their own version to do more work than the AT&T standard includes. If you are using the AT&T C++ standard, your program should successfully run on any other computer that also uses AT&T C++.
EXAMPLE
 AT&T
developed C++ as an improved version of the C pro- gramming language.
C has been around since the 1970s and has matured into a solid,
extremely popular programming language. ANSI, the American National
Standards Institute, established a standard C programming
specification called ANSI C. If your C compiler conforms to ANSI C,
your program will work on any other computer that also has ANSI C.
This compatibility between comput- ers is so important that AT&T’s C++
3.0 standard includes almost every element of the ANSI C, plus more.
In fact, the ANSI C committee often requires that a C++ feature be
included in subse- quent versions of C. For instance, function
prototypes, a feature not found in older versions of ANSI C, is now a
requirement for approval by the ANSI committee. Function prototypes
did not exist until AT&T required them in their early C++
specification.
AT&T
developed C++ as an improved version of the C pro- gramming language.
C has been around since the 1970s and has matured into a solid,
extremely popular programming language. ANSI, the American National
Standards Institute, established a standard C programming
specification called ANSI C. If your C compiler conforms to ANSI C,
your program will work on any other computer that also has ANSI C.
This compatibility between comput- ers is so important that AT&T’s C++
3.0 standard includes almost every element of the ANSI C, plus more.
In fact, the ANSI C committee often requires that a C++ feature be
included in subse- quent versions of C. For instance, function
prototypes, a feature not found in older versions of ANSI C, is now a
requirement for approval by the ANSI committee. Function prototypes
did not exist until AT&T required them in their early C++
specification.
C++ By Example teaches you to program in C++. All programs
conform to the AT&T C++ 2.1 standard. The differences between AT&T 2.1 and 3.0 are relatively minor for beginning programmers. As you progress in your programming skills, you will want to tackle the more advanced aspects of C++ and Version 3.0 will come more into play later. Whether you use a PC, a minicomputer, a mainframe, or a supercomputer, the C++ language you learn here should work on any that conform to AT&T C++ 2.1 and later.
There is a debate in the programming community as to whether a person should learn C before C++ or learn only C++. Because C++ is termed a “better C,” many feel that C++ is an important language in its own right and can be learned just as easily as C. Actually, C++ pundits state that C++ teaches better programming habits than the plain, “vanilla” C. This book is aimed at the beginner programmer, and the author feels that C++ is a great language with which to begin. If you were to first learn C, you would have to “unlearn” a few things when you moved to C++. This book attempts to use the C++ language elements that are better than C. If you are new to program- ming, you learn C++ from the start. If you have a C background, you learn that C++ overcomes many of C’s limitations.
When some people attempt to learn C++ (and C), even if they
are programmers in other computer languages, they find that C++ can be cryptic and difficult to understand. This does not have to be the case. When taught to write clear and concise C++ code in an order that builds on fundamental programming concepts,
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
programmers find that C++ is no more difficult to learn or use than any other programming language. Actually, after you start using it, C++’s modularity makes it even easier to use than most other languages. Once you master the programming elements this book teaches you, you will be ready for the advanced power for which C++ was designed —object-oriented programming (OOP). The last chapter of this book, “Introduction to Object-Oriented Program- ming,” offers you the springboard to move to this exciting way of writing programs.
Even if you’ve never programmed a computer before, you will soon understand that programming in C++ is rewarding. Becoming an expert programmer in C++ — or in any other computer lan- guage—takes time and dedication. Nevertheless, you can start writing simple programs with little effort. After you learn the fundamentals of C++ programming, you can build on what you learn and hone your skills as you write more powerful programs. You also might see new uses for your computer and develop programs others can use.
The importance of C++ cannot be overemphasized. Over the years, several programming languages were designed to be “the only programming language you would ever need.” PL/ I was heralded as such in the early 1960s. It turned out to be so large and took so many system resources that it simply became another language programmers used, along with COBOL, FORTRAN, and many others. In the mid-1970s, Pascal was developed for smaller computers. Microcomputers had just been invented, and the Pascal language was small enough to fit in their limited memory space while still offering advantages over many other languages. Pascal became popular and is still used often today, but it never became the answer for all programming tasks, and it failed at being “the only programming language you would ever need.”
When the mass computer markets became familiar with C in
the late 1970s, C also was promoted as “the only programming language you would ever need.” What has surprised so many skeptics (including this author) is that C has practically fulfilled this promise! An incredible number of programming shops have con- verted to C. The appeal of C’s efficiency, combined with its portabil- ity among computers, makes it the language of choice. Most of
EXAMPLE
today’s familiar spreadsheets, databases, and word processors are written in C. Now that C++ has improved on C, programmers are retooling their minds to think in C++ as well.
 The
programmer help-wanted ads seek more and more C++ programmers every
day. By learning this popular language, you will be learning the
latest direction of programming and keeping your skills current with
the market. You have taken the first step: with this book, you learn
the C++ language particulars as well as many programming tips to use
and pitfalls to avoid. This book attempts to teach you to be not just
a C++ programmer, but a better programmer by applying the structured,
long-term programming habits that professionals require in today’s
business and industry.
The
programmer help-wanted ads seek more and more C++ programmers every
day. By learning this popular language, you will be learning the
latest direction of programming and keeping your skills current with
the market. You have taken the first step: with this book, you learn
the C++ language particulars as well as many programming tips to use
and pitfalls to avoid. This book attempts to teach you to be not just
a C++ programmer, but a better programmer by applying the structured,
long-term programming habits that professionals require in today’s
business and industry.
The Background of C+ +
The UNIX operating system was written almost entirely in C.
Before you jump into C++, you might find it helpful to know a little about the evolution of the C++ programming language. C++ is so deeply rooted in C that you should first see where C began. Bell Labs first developed the C programming language in the early 1970s, primarily so Bell programmers could write their UNIX oper- ating system for a new DEC (Digital Equipment Corporation) com- puter. Until that time, operating systems were written in assembly language, which is tedious, time-consuming, and difficult to main- tain. The Bell Labs people knew they needed a higher-level pro- gramming language to implement their project quicker and create code that was easier to maintain.
Because other high-level languages at the time (COBOL, FOR- TRAN, PL/ I, and Algol) were too slow for an operating system’s code, the Bell Labs programmers decided to write their own lan- guage. They based their new language on Algol and BCPL. Algol is still used in the European markets, but is not used much in America. BCPL strongly influenced C, although it did not offer the various data types that the makers of C required. After a few versions, these Bell programmers developed a language that met their goals well. C is efficient (it is sometimes called a high, low-level language due to its speed of execution), flexible, and contains the proper language elements that enable it to be maintained over time.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
In the 1980s, Bjourn Stroustrup, working for AT&T, took the C language to its next progression. Mr. Stroustrup added features to compensate for some of the pitfalls C allowed and changed the way programmers view programs by adding object-orientation to the language. The object-orientation aspect of programming started in other languages, such as Smalltalk. Mr. Stroustrup realized that C++ programmers needed the flexibility and modularity offered by a true OOP programming language.
C++ Compared with Othe r Languages
C++ requires more stringent data-type checking than does C.
If you have programmed before, you should understand a little about how C++ differs from other programming languages on the market. C++ is efficient and has much stronger typing than its C predecessor. C is known as a weakly typed language; variable data types do not necessarily have to hold the same type of data. (Func- tion prototyping and type casting help to alleviate this problem.)
For example, if you declare an integer variable and decide to put a character value in it, C enables you to do so. The data might not be in the format you expect, but C does its best. This is much different from stronger-typed languages such as COBOL and Pascal.
If this discussion seems a little over your head at this point, relax. The upcoming chapters will elaborate on these topics and provide many examples.
C++ is a small, block-structured programming language. It has fewer than 46 keywords. To compensate for its small vocabulary, C++ has one of the largest assortment of operators such as +, - , and && (second only to APL). The large number of operators in C++ might tempt programmers to write cryptic programs that have only a small amount of code. As you learn throughout this book, however, you will find that making the program more readable is more important than saving some bytes. This book teaches you how to use the C++ operators to their fullest extent, while maintaining readable programs.
C++’s large number of operators (almost equal to the number of keywords) requires a more judicious use of an operator precedence
EXAMPLE
table. Appendix D, “C++ Precedence Table,” includes the C++ operator precedence table. Unlike most other languages that have only four or five levels of precedence, C++ has 15. As you learn C++, you have to master each of these 15 levels. This is not as difficult as it sounds, but its importance cannot be overstated.
 C++
also has no input or output statements. You might want to read that
sentence again! C++ has no commands that perform input or output. This
is one of the most important reasons why C++ is available on so many
different computers. The I/ O (input/ output) statements of most
languages tie those languages to specific hard- ware. BASIC, for
instance, has almost twenty I/ O commands— some of which write to the
screen, to the printer, to a modem, and so forth. If you write a BASIC
program for a microcomputer, chances are good that it cannot run on a
mainframe without considerable modification.
C++
also has no input or output statements. You might want to read that
sentence again! C++ has no commands that perform input or output. This
is one of the most important reasons why C++ is available on so many
different computers. The I/ O (input/ output) statements of most
languages tie those languages to specific hard- ware. BASIC, for
instance, has almost twenty I/ O commands— some of which write to the
screen, to the printer, to a modem, and so forth. If you write a BASIC
program for a microcomputer, chances are good that it cannot run on a
mainframe without considerable modification.
C++’s input and output are performed through the abundant use of operators and function calls. With every C++ compiler comes a library of standard I/ O functions. I/ O functions are hardware independent, because they work on any device and on any computer that conform to the AT&T C++ standard.
To master C++ completely, you have to be more aware of your computer’s hardware than most other languages would require you to be. You certainly do not have to be a hardware expert, but understanding the internal data representation makes C++ much more usable and meaningful.
It also helps if you can become familiar with binary and hexadecimal numbers. You might want to read Appendix A, “Memory Addressing, Binary, and Hexadecimal Review,” for a tutorial on these topics before you start to learn the C++ language. If you do not want to learn these topics, you can still become a good C++ programmer, but knowing what goes on “under the hood” makes C++ more meaningful to you as you learn it.
C++ and Microcomputer s
C was a relatively unknown language until it was placed on the microcomputer. With the invention and growth of the microcom- puter, C blossomed into a worldwide computer language. C++
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
extends that use on smaller computers. Most of readers of C++ By Example are probably working on a microcomputer-based C++ system. If you are new to computers, this section will help you learn how microcomputers were developed.
In the 1970s, NASA created the microchip, a tiny wafer of sili- con that occupies a space smaller than a postage stamp. Computer components were placed on these microchips, hence computers required much less space than before. NASA produced these smaller computers in response to their need to send rocket ships to the moon with on-board computers. The computers on Earth could not provide split-second accuracy for rockets because radio waves took several seconds to travel between the Earth and the moon. Through development, these microchips became small enough so the computers could travel with a rocket and safely compute the rocket’s trajectory.
The space program was not the only beneficiary of computer miniaturization. Because microchips became the heart of the mi- crocomputer, computers could now fit on desktops. These micro- computers cost much less than their larger counterparts, so many people started buying them. Thus, the home and small-business computer market was born.
Today, microcomputers are typically called PCs from the wide- spread use of the original IBM PC. The early PCs did not have the memory capacity of the large computers used by government and big business. Nevertheless, PC owners still needed a way to pro- gram these machines. BASIC was the first programming language used on PCs. Over the years, many other languages were ported from larger computers to the PC. However, no language was as successful as C in becoming the worldwide standard programming language. C++ seems to be the next standard.
Before diving into C++, you might take a few moments to familiarize yourself with some of the hardware and software com- ponents of your PC. The next section, “An Overview of Your Computer,” introduces you to computer components that C++ interacts with, such as the operating system, memory, disks, and I/ O devices. If you are already familiar with your computer’s hardware and software, you might want to skip to Chapter 2, “What Is a Program?,” and begin using C++.
EXAMPLE
An Overview of You r Computer
 Your
computer system consists of two parts: hardware and software. The
hardware consists of all the physical parts of the machine. Hardware
has been defined as “anything you can kick.” Although this definition
is coarse, it illustrates that your computer’s hardware consists of
the physical components of your PC. The software is everything else.
Software comprises the programs and data that interact with your
hardware. The C++ language is an example of software. You can use C++
to create even more software programs and data.
Your
computer system consists of two parts: hardware and software. The
hardware consists of all the physical parts of the machine. Hardware
has been defined as “anything you can kick.” Although this definition
is coarse, it illustrates that your computer’s hardware consists of
the physical components of your PC. The software is everything else.
Software comprises the programs and data that interact with your
hardware. The C++ language is an example of software. You can use C++
to create even more software programs and data.
Hardware
Figure 1.1 shows you a typical PC system. Before using C++, you should have a general understanding of what hardware is and how your hardware components work together.
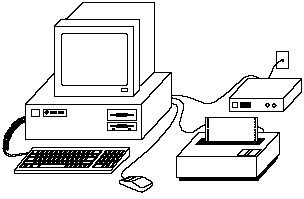 Monitor
Monitor
System Unit
Disk Drives
Keyboard Mouse Printer
Modem
Figure 1.1. A typical PC system.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
A byte is a single
The System Unit and Memor y
The system unit is the large, box-shaped component of the computer. This unit houses the PC’s microprocessor. You might hear the microprocessor called the CPU, or central processing unit. The CPU acts like a traffic cop, directing the flow of information throughout your computer system. The CPU is analogous also to the human brain. When you use a computer, you are actually interact- ing with its CPU. All the other hardware exists so the CPU can send information to you (through the monitor or the printer), and you can give instructions to the CPU (through the keyboard or the mouse). The CPU also houses the computer’s internal memory. Al- though the memory has several names, it is commonly referred to as RAM (random-access memory). RAM is where the CPU looks for software and data. When you run a C++ program, for example, you are instructing your computer’s CPU to look in RAM for that program and carry out its instructions. C++ uses RAM space when
it is loaded.
RAM is used for many things and is one of the most important
character of memory.
components of your computer’s hardware. Without RAM, your computer would have no place for its instructions and data. The amount of RAM can also affect the computer’s speed. In general, the more RAM your computer has, the more work it can do and the faster it can process data.
The amount of RAM is measured by the number of characters it can hold. PCs generally hold approximately 640,000 characters of RAM. A character in computer terminology is called a byte, and a byte can be a letter, a number, or a special character such as an exclamation point or a question mark. If your computer has 640,000 bytes of RAM, it can hold a total of 640,000 characters.
All the zeros following RAM measurements can become cum- bersome. You often see the shortcut notation K (which comes from the metric system’s kilo, meaning 1000) in place of the last three zeros. In computer terms, K means exactly 1024 bytes; but this number is usually rounded to 1000 to make it easier to remember. Therefore, 640K represents approximately 640,000 bytes of RAM. For more information, see the sidebar titled “The Power of Two.”
The limitations of RAM are similar to the limitations of audio cassette tapes. If a cassette is manufactured to hold 60 minutes of
EXAMPLE
music, it cannot hold 75 minutes of music. Likewise, the total number of characters that compose your program, the C++ data, and your computer’s system programs cannot exceed the RAM’s limit (unless you save some of the characters to disk).
 You
want as much RAM as possible to hold C++, data, and the system
programs. Generally, 640K is ample room for anything you might want to
do in C++. Computer RAM is relatively inexpensive, so if your computer
has less than 640K bytes of memory, you should consider purchasing
additional memory to increase the total RAM to 640K. You can put more
than 640K in most PCs. There are two types of additional RAM:
extended memory and expanded memory (they both offer memory
capacity greater than 640K). You can access this extra RAM with some
C++ systems, but most beginning C++ programmers have no need to worry
about RAM beyond 640K.
You
want as much RAM as possible to hold C++, data, and the system
programs. Generally, 640K is ample room for anything you might want to
do in C++. Computer RAM is relatively inexpensive, so if your computer
has less than 640K bytes of memory, you should consider purchasing
additional memory to increase the total RAM to 640K. You can put more
than 640K in most PCs. There are two types of additional RAM:
extended memory and expanded memory (they both offer memory
capacity greater than 640K). You can access this extra RAM with some
C++ systems, but most beginning C++ programmers have no need to worry
about RAM beyond 640K.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
The computer stores C++ programs to RAM as you write them. If you have used a word processor before, you have used RAM. As you type words in your word-processed documents, your words appear on the video screen and also go to RAM for storage.
Despite its importance, RAM is only one type of memory in your computer. RAM is volatile; when you turn the computer off, all RAM is erased. Therefore, you must store the contents of RAM to a nonvolatile, more permanent memory device (such as a disk) before you turn off your computer. Otherwise, you lose your work.
Disk Storag e
A disk is another type of computer memory, sometimes called external memory. Disk storage is nonvolatile. When you turn off your computer, the disk’s contents do not go away. This is important. After typing a long C++ program in RAM, you do not want to retype the same program every time you turn your computer back on. Therefore, after creating a C++ program, you save the program to disk, where it remains until you’re ready to retrieve it again.
Disk storage differs from RAM in ways other than volatility. Disk storage cannot be processed by the CPU. If you have a program or data on disk that you want to use, you must transfer it from the disk to RAM. This is the only way the CPU can work with the program or data. Luckily, most disks hold many times more data than the RAM’s 640K. Therefore, if you fill up RAM, you can store its contents on disk and continue working. As RAM continues to fill up, you or your C++ program can keep storing the contents of RAM to the disk.
This process might sound complicated, but you have only to understand that data must be transferred to RAM before your computer can process it, and saved to disk before you shut your computer off. Most the time, a C++ program runs in RAM and retrieves data from the disk as it needs it. In Chapter 30, “Sequential Files,” you learn that working with disk files is not difficult.
There are two types of disks: hard disks and floppy disks. Hard disks (sometimes called fixed disks) hold much more data and are many times faster to work with than floppy disks. Most of your C++ programs and data should be stored on your hard disk. Floppy disks
EXAMPLE
 are good for
backing up hard disks, and for transferring data and programs from one
computer to another. (These removable floppy disks are often called
diskettes.) Figure 1.2 shows two common sizes, the 5 1/ 4-inch disk
and the 3 1/ 2-inch disk. These disks can hold from 360K to 1.4
million bytes of data.
are good for
backing up hard disks, and for transferring data and programs from one
computer to another. (These removable floppy disks are often called
diskettes.) Figure 1.2 shows two common sizes, the 5 1/ 4-inch disk
and the 3 1/ 2-inch disk. These disks can hold from 360K to 1.4
million bytes of data.
Write-protect notch
 Figure
1.2. 5 1/4-inch disk and 3 1/2-inch disk.
Figure
1.2. 5 1/4-inch disk and 3 1/2-inch disk.
Before using a new box of disks, you have to format them (unless you buy disks that are already formatted). Formatting prepares the disks for use on your computer by writing a pattern of paths, called tracks, where your data and programs are stored. Refer to the operating system instruction manual for the correct format- ting procedure.
Disk drives house the disks in your computer. Usually, the disk drives are stored in your system unit. The hard disk is sealed inside the hard disk drive, and you never remove it (except for repairs). In general, the floppy disk drives also are contained in the system unit, but you insert and remove these disks manually.
Disk drives have names. The computer’s first floppy disk drive is called drive A. The second floppy disk drive, if you have one, is called drive B. The first hard disk (many computers have only one) is called drive C. If you have more than one hard disk, or if your hard disk is logically divided into more than one, the others are named drive D, drive E, and so on.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
Disk size is measured in bytes, just as RAM is. Disks can hold many millions of bytes of data. A 60-million-byte hard disk is common. In computer terminology, a million bytes is called a megabyte, or M. Therefore, if you have a 60-megabyte hard disk, it can hold approximately 60 million characters of data before it runs out of space.
The Monito r
The television-like screen is called the monitor. Sometimes the monitor is called the CRT (which stands for the primary component of the monitor, the cathode-ray tube). The monitor is one place where the output of the computer can be sent. When you want to look at a list of names and addresses, you could write a C++ program to list the information on the monitor.
The advantage of screen output over printing is that screen output is faster and does not waste paper. Screen output, however, is not permanent. When text is scrolled off-screen (displaced by additional text coming on-screen), it is gone and you might not always be able to see it again.
All monitors have a cursor, which is a character such as a blinking underline or a rectangle. The cursor moves when you type letters on-screen, and always indicates the location of the next character to be typed.
Monitors that can display pictures are called graphics monitors. Most PC monitors are capable of displaying graphics and text, but some can display only text. If your monitor cannot display colors, it is called a monochrome monitor.
Your monitor plugs into a display adapter located in your system unit. The display adapter determines the amount of resolution and number of possible on-screen colors. Resolution refers to the number of row and column intersections. The higher the resolution, the more rows and columns are present on your screen and the sharper your text and graphics appear. Some common display adapters are MCGA, CGA, EGA, and VGA.
EXAMPLE
The Printe r
The printer provides a more permanent way of recording your computer’s results. It is the “typewriter” of the computer. Your printer can print C++ program output to paper. Generally, you can print anything that appears on your screen. You can use your printer to print checks and envelopes too, because most types of paper work with computer printers.
 The
two most common PC printers are the dot-matrix printer and the
laser printer. A dot-matrix printer is inexpensive, fast, and uses a
series of small dots to represent printed text and graphics. A laser
printer is faster than a dot-matrix, and its output is much sharper
because a laser beam burns toner ink into the paper. For many people,
a dot-matrix printer provides all the speed and quality they need for
most applications. C++ can send output to either type of printer.
The
two most common PC printers are the dot-matrix printer and the
laser printer. A dot-matrix printer is inexpensive, fast, and uses a
series of small dots to represent printed text and graphics. A laser
printer is faster than a dot-matrix, and its output is much sharper
because a laser beam burns toner ink into the paper. For many people,
a dot-matrix printer provides all the speed and quality they need for
most applications. C++ can send output to either type of printer.
The Keyboar d
Figure 1.3 shows a typical PC keyboard. Most the keys are the same as those on a standard typewriter. The letter and number keys in the center of the keyboard produce their indicated characters on- screen. If you want to type an uppercase letter, be sure to press one of the Shift keys before typing the letter. Pressing the CapsLock key shifts the keyboard to an uppercase mode. If you want to type one of the special characters above a number, however, you must do so with the Shift key. For instance, to type the percent sign (%), you would press Shift-5.
Like the Shift keys, the Alt and Ctrl keys can be used with some other keys. Some C++ programs require that you press Alt or Ctrl before pressing another key. For instance, if your C++ program prompts you to press Alt-F, you should press the Alt key, then press F while still holding down Alt, then release both keys. Do not hold them both down for long, however, or the computer keeps repeating your keystrokes as if you typed them more than once.
The key marked Esc is called the escape key. In many C++ programs, you can press Esc to “escape,” or exit from, something you started and then wanted to stop. For example, if you prompt your C++ compiler for help and you no longer need the help
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
message, you can press Esc to remove the help message from the screen.
Escape
Tab
Control
Backslash (\) Backspace
Enter
 Tab
Tab
Figure 1.3. The various PC keyboards.
EXAMPLE
 The
group of numbers and arrows on the far right of the keyboard is called
the numeric keypad. People familiar with a 10-key adding machine
usually prefer to type numbers from the keypad rather than from the
top row of the alphabetic key section. The numbers on the keypad work
only when you press the NumLock key. If you press NumLock a second
time, you disable these number keys and make the arrow keys work
again. To prevent confusion, many keyboards have separate arrow keys
and a keypad used solely for numbers.
The
group of numbers and arrows on the far right of the keyboard is called
the numeric keypad. People familiar with a 10-key adding machine
usually prefer to type numbers from the keypad rather than from the
top row of the alphabetic key section. The numbers on the keypad work
only when you press the NumLock key. If you press NumLock a second
time, you disable these number keys and make the arrow keys work
again. To prevent confusion, many keyboards have separate arrow keys
and a keypad used solely for numbers.
The arrows help you move the cursor from one area of the screen to another. To move the cursor toward the top of the screen, you have to press the up arrow continuously. To move the cursor to the right, you press the right-arrow, and so on. Do not confuse the Backspace key with the left-arrow. Pressing Backspace moves the cursor backward one character at a time—erasing everything as it moves. The left-arrow simply moves the cursor backward, without erasing.
The keys marked Insert and Delete (Ins and Del on some keyboards) are useful for editing. Your C++ program editor prob- ably takes advantage of these two keys. Insert and Delete work on C++ programs in the same way they work on a word processor’s text. If you do not have separate keys labeled Insert and Delete, you probably have to press NumLock and use the keypad key 0 (for Insert) and period (for Delete).
PgUp and PgDn are the keys to press when you want to scroll the screen (that is, move your on-screen text either up or down). Your screen acts like a camera that pans up and down your C++ programs. You can move the screen down your text by pressing PgDn, and up by pressing PgUp. (Like Insert and Delete, you might have to use the keypad for these operations.)
The keys labeled F1 through F12 (some keyboards go only to F10) are called function keys. The function keys are located either across the top of the alphabetic section or to the left of it. These keys perform an advanced function, and when you press one of them, you usually want to issue a complex command, such as searching for a specific word in a program. The function keys in your C++ program, however, do not necessarily produce the same results as they might in another program, such as a word processor. In other words, function keys are application-specific.
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++

The Mous e
The mouse is a relatively new input device. The mouse moves the cursor to any on-screen location. If you have never used a mouse before, you should take a little time to become skillful in moving the cursor with it. Your C++ editor (described in Chapter 2, “What is a Program?”) might use the mouse for selecting commands from its menus.
Mouse devices have two or three buttons. Most of the time, pressing the third button produces the same results as simulta- neously pressing both keys on a two-button mouse.
A modem can be used to communi- cate between two distant computers.
The Mode m
A PC modem enables your PC to communicate with other computers over telephone lines. Some modems, called external modems, sit in a box outside your computer. Internal modems reside inside the system unit. It does not matter which one you have, because they operate identically.
Some people have modems so they can share data between their computer and that of a long-distance friend or off-site co- worker. You can write programs in C++ that communicate with your modem.
EXAMPLE

Software
No matter how fast, large, and powerful your computer’s hardware is, its software determines what work is done and how the computer does it. Software is to a computer what music is to a stereo system. You store software on the computer’s disk and load it in your computer’s memory when you are ready to process the soft- ware, just as you store music on a tape and play it when you want to hear music.
Programs and Dat a
No doubt you have heard the phrase, data processing. This is what computers actually do: they take data and manipulate it into
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
meaningful output. The meaningful output is called information. Figure 1.4 shows the input-process-output model, which is the foun- dation of everything that happens in your computer.
 Figure
Figure
In Chapter 2, “What Is a Program?,” you learn the mechanics of programs. For now, you should know that the programs you write in C++ process the data that you input in the programs. Both data and programs compose the software. The hardware acts as a vehicle to gather the input and produce the output. Without software, computers would be worthless, just as an expensive stereo would be useless without some way of playing music so you can hear it.
The input comes from input devices, such as keyboards, mo- dems, and disk drives. The CPU processes the input and sends the results to the output devices, such as the printer and the monitor. A C++ payroll program might receive its input (the hours worked) from the keyboard. It would instruct the CPU to calculate the payroll amounts for each employee in the disk files. After processing the payroll, the program could print the checks.
MS-DOS
MS-DOS (Microsoft disk operating system) is a system that lets your C++ programs interact with hardware. MS-DOS (commonly called DOS) is always loaded into RAM when you turn on your computer. DOS controls more than just the disks; DOS is there so your programs can communicate with all the computer’s hardware, including the monitor, keyboard, and printer.
Figure 1.5 illustrates the concept of DOS as the “go-between” with your computer’s hardware and software. Because DOS under- stands how to control every device hooked to your computer, it stays in RAM and waits for a hardware request. For instance, printing the words “ C++ i s f un ! ” on your printer takes many computer instructions. However, you do not have to worry about all
EXAMPLE
those instructions. When your C++ program wants to print some- thing, it tells DOS to print it. DOS always knows how to send information to your printer, so it takes your C++ program requests and does the work of routing that data to the printer.
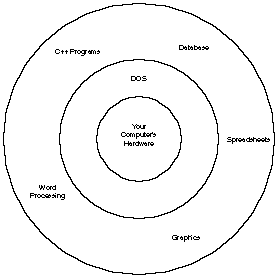

Figure 1.5. DOS interfaces between hardware and software.
Many people program computers for years and never take the time to learn why DOS is there. You do not have to be an expert in DOS, or even know more than a few simple DOS commands, to be proficient with your PC. Nevertheless, DOS does some things that C++ cannot do, such as formatting disks and copying files to your disks. As you learn more about the computer, you might see the need to better understand DOS. For a good introduction to using DOS, refer to the book MS-DOS 5 QuickStart (Que).
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++

Figure 1.6 shows you the placement of DOS, C++, and your C++ data area in RAM. This formation is a typical way to represent RAM— several boxes stacked on top of each other. Each memory location (each byte) has a unique address, just as everybody’s resi- dence has a unique address. The first address in memory begins at 0, the second RAM address is 1, and so on until the last RAM location, many thousands of bytes later.

Figure 1.6. After MS-DOS and a C++ program, there is less RAM for data.
Your operating system (whether you use MS-DOS, PC DOS, DR DOS, or UNIX) takes part of the first few thousand bytes of memory. The amount of RAM that DOS takes varies with each computer’s configuration. When working in C++, the C++ system sits on top of DOS, leaving you with the remainder of RAM for your program and data. This explains why you might have a total of 512K of RAM and still not have enough memory to run some programs— DOS is using some of the RAM for itself.
EXAMPLE
Review Question s
The answers to each chapter’s review questions are in Appen- dix B, aptly named “Answers to Review Questions.”
-
 What
Whatis the name of one of the programming languages from which C was developed?
-
 True
Trueor false: C++ is known as a “better C.”
-
In what decade was C++ developed?
-
True or false: C++ is too large to fit on many micro- computers.
-
Which usually holds more data: RAM or the hard disk?
-
What device is needed for your PC to communicate over telephone
lines?
-
 Which
Whichof the following device types best describes the mouse?
-
Storage
-
Input
-
Output
-
Processing
-
-
What key would you press to turn off the numbers on the numeric
keypad?
-
 What
Whatoperating system is written almost entirely in C?
-
Why is RAM considered volatile?
-
True or false: The greater the resolution, the better the appearance
of graphics on-screen.
-
How many bytes is 512K?
-
What does modem stand for?
Chapter 1 ♦ Welcome to C++
Summary
C++ is an efficient, powerful, and popular programming lan- guage. Whether you are new to C++ or an experienced programmer, C++ is all you need to program the computer to work the way you want it to.
This chapter presented the background of C++ by walking you through the history of its predecessor, the C programming lan- guage. C++ adds to C and offers some of the most advanced programming language commands that exist today.
The rest of this book is devoted to teaching you C++. Chapter 2, “What Is a Program?,” explains program concepts so you can begin to write C++ programs.

 What Is a
Program?
What Is a
Program?
This chapter introduces you to fundamental programming con- cepts. The task of programming computers has been described as rewarding, challenging, easy, difficult, fast, and slow. Actually, it is a combination of all these descriptions. Writing complex programs to solve advanced problems can be frustrating and time-consuming, but you can have fun along the way, especially with the rich assortment of features that C++ has to offer.
This chapter also describes the concept of programming, from a program’s inception to its execution on your computer. The most difficult part of programming is breaking the problem into logical steps that the computer can execute. Before you finish this chapter, you will type and execute your first C++ program.
This chapter introduces you to
-
The concept of programming
-
The program’s output
-
Program design
-
Using an editor
-
Using a compiler
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
-
Typing and running a C++ program
-
Handling errors
After you complete this chapter, you should be ready to learn the C++ programming language elements in greater detail.
Computer Program s
Before you can make C++ work for you, you must write a C++ program. You have seen the word program used several times in this book. The following note defines a program more formally.

Keep in mind that computers are only machines. They’re not smart; in fact, they’re quite the opposite! They don’t do anything until they are given detailed instructions. A word processor, for example, is a program somebody wrote—in a language such as C++—that tells your computer exactly how to behave when you type words into it.
You are familiar with the concept of programming if you have ever followed a recipe, which is a “program,” or a list of instructions, telling you how to prepare a certain dish. A good recipe lists these instructions in their proper order and with enough description so you can carry out the directions successfully, without assuming anything.
If you want your computer to help with your budget, keep track of names and addresses, or compute your gas mileage, it needs a program to tell it how to do those things. You can supply that program in two ways: buy a program somebody else wrote, or write the program yourself.
Writing the program yourself has a big advantage for many applications: The program does exactly what you want it to do. If you buy one that is already written, you have to adapt your needs to those of the author of the program. This is where C++ comes into
EXAMPLE
play. With the C++ programming language (and a little studying), you can make your computer carry out your own tasks precisely.
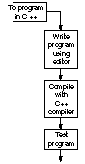 To
give C++ programming instructions to your computer, you need an
editor and a C++ compiler. An editor is similar to a word
processor; it is a program that enables you to type a C++ program into
memory, make changes (such as moving, copying, inserting, and deleting
text), and save the program more permanently in a disk file. After you
use the editor to type the program, you must compile it before you can
run it.
To
give C++ programming instructions to your computer, you need an
editor and a C++ compiler. An editor is similar to a word
processor; it is a program that enables you to type a C++ program into
memory, make changes (such as moving, copying, inserting, and deleting
text), and save the program more permanently in a disk file. After you
use the editor to type the program, you must compile it before you can
run it.
 The
C++ programming language is called a compiled language. You cannot
write a C++ program and run it on your computer unless you have a C++
compiler. This compiler takes your C++ language instructions and
translates them into a form that your computer can read. A C++
compiler is the tool your computer uses to understand the C++ language
instructions in your programs. Many compilers come with their own
built-in editor. If yours does, you probably feel that your C++
programming is more integrated.
The
C++ programming language is called a compiled language. You cannot
write a C++ program and run it on your computer unless you have a C++
compiler. This compiler takes your C++ language instructions and
translates them into a form that your computer can read. A C++
compiler is the tool your computer uses to understand the C++ language
instructions in your programs. Many compilers come with their own
built-in editor. If yours does, you probably feel that your C++
programming is more integrated.
To some beginning programmers, the process of compiling a program before running it might seem like an added and meaning- less step. If you know the BASIC programming language, you might not have heard of a compiler or understand the need for one. That’s because BASIC (also APL and some versions of other computer languages) is not a compiled language, but an interpreted language. Instead of translating the entire program into machine-readable form (as a compiler does in one step), an interpreter translates each program instruction—then executes it—before translating the next one. The difference between the two is subtle, but the bottom line is not: Compilers produce much more efficient and faster-running programs than interpreters do. This seemingly extra step of compil- ing is worth the effort (and with today’s compilers, there is not much extra effort needed).
Because computers are machines that do not think, the instruc-
tions you write in C++ must be detailed. You cannot assume your computer understands what to do if some instruction is not in your program, or if you write an instruction that does not conform to C++ language requirements.
After you write and compile a C++ program, you have to run,
or execute, it. Otherwise, your computer would not know that you
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
want it to follow the instructions in the program. Just as a cook must follow a recipe’s instructions before making the dish, so too your computer must execute a program’s instructions before it can ac- complish what you want it to do. When you run a program, you are telling the computer to carry out your instructions.
Design your
Program Desig n
You must plan your programs before typing them into your
programs before you type them.
C++ editor. When builders construct houses, for example, they don’t immediately grab their lumber and tools and start building! They first find out what the owner of the house wants, then they draw up the plans, order the materials, gather the workers, and finally start building the house.
The hardest part of writing a program is breaking it into logical steps that the computer can follow. Learning the C++ language is a requirement, but it is not the only thing to consider. There is a method of writing programs, a formal procedure you should learn, that makes your programming job easier. To write a program you should:
-
Define the problem to be solved with the computer.
-
Design the program’s output (what the user should see).
EXAMPLE
-
Break the problem into logical steps to achieve this output.
-
Write the program (using the editor).
-
Compile the program.
-
Test the program to assure it performs as you expect.
As you can see from this procedure, the typing of your program occurs toward the end of your programming. This is important, because you first have to plan how to tell the computer how to perform each task.
 Your
computer can perform instructions only step-by-step. You must assume
that your computer has no previous knowledge of the problem, so it is
up to you to provide that knowledge, which, after all, is what a good
recipe does. It would be a useless recipe for a cake if all it said
was: “Bake the cake.” Why? Because this assumes too much on the part
of the baker. Even if you write the recipe in step-by-step fashion,
proper care must be taken (through planning) to be sure the steps are
in sequence. Wouldn’t it be foolish also to instruct a baker to put
the ingredients into the oven before stirring them?
Your
computer can perform instructions only step-by-step. You must assume
that your computer has no previous knowledge of the problem, so it is
up to you to provide that knowledge, which, after all, is what a good
recipe does. It would be a useless recipe for a cake if all it said
was: “Bake the cake.” Why? Because this assumes too much on the part
of the baker. Even if you write the recipe in step-by-step fashion,
proper care must be taken (through planning) to be sure the steps are
in sequence. Wouldn’t it be foolish also to instruct a baker to put
the ingredients into the oven before stirring them?
This book adheres to the preceding programming procedure throughout the book, as each program appears. Before you see the actual program, the thought process required to write the program appears. The goals of the program are presented first, then these goals are broken into logical steps, and finally the program is written.
Designing the program in advance guarantees that the entire program structure is more accurate and keeps you from having to make changes later. A builder, for example, knows that a room is much harder to add after the house is built. If you do not properly plan every step, it is going to take you longer to create the final, working program. It is always more difficult to make major changes after you write your program.
Planning and developing according to these six steps becomes much more important as you write longer and more complicated programs. Throughout this book, you learn helpful tips for program design. Now it’s time to launch into C++, so you can experience the satisfaction of typing your own program and seeing it run.
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
Using a Program Edito r
The instructions in your C++ program are called the source code. You type source code into your computer’s memory by using your program editor. After you type your C++ source code (your pro- gram), you should save it to a disk file before compiling and running the program. Most C++ compilers expect C++ source programs to be stored in files with names ending in .CPP. For example, the follow- ing are valid filenames for most C++ compilers:
MYPROG.CPP SALESACT.CPP EMPLYEE.CPP ACCREC.CPP
Many C++ compilers include a built-in editor. Two of the most popular C++ compilers (both conform to the AT&T C++ 2.1 stan- dard and include their own extended language elements) are Borland’s C++ and Microsoft’s C/ C++ 7.0 compilers. These two programs run in fully integrated environments that relieve the programmer from having to worry about finding a separate pro- gram editor or learning many compiler-specific commands.
Figure 2.1 shows a Borland C++ screen. Across the top of the screen (as with Microsoft C/ C++ 7.0) is a menu that offers pull- down editing, compiling, and running options. The middle of the screen contains the body of the program editor, and this is the area where the program goes. From this screen, you type, edit, compile, and run your C++ source programs. Without an integrated environ- ment, you would have to start an editor, type your program, save the program to disk, exit the editor, run the compiler, and only then run the compiled program from the operating system. With Borland’s C++ and Microsoft C/ C++ 7.0, you simply type the program into the editor, then—in one step—you select the proper menu option that compiles and runs the program.
EXAMPLE
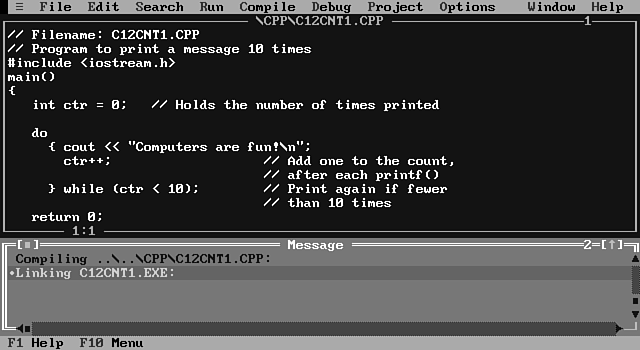
 Figure
2.1. Borland Turbo C++’s integrated environment.
Figure
2.1. Borland Turbo C++’s integrated environment.
If you do not own an integrated environment such as Borland C++ or Microsoft C/ C++, you have to find a program editor. Word processors can act as editors, but you have to learn how to save and load files in a true ASCII text format. It is often easier to use an editor than it is to make a word processor work like one.
On PCs, DOS Version 5 comes with a nice, full-screen editor called EDIT. It offers menu-driven commands and full cursor- control capabilities. EDIT is a simple program to use, and is a good beginner’s program editor. Refer to your DOS manual or a good book on DOS, such as MS-DOS 5 QuickStart (Que), for more infor- mation on this program editor.
Another editor, called EDLIN, is available for earlier versions of DOS. EDLIN is a line editor that does not allow full-screen cursor control, and it requires you to learn some cryptic commands. The advantage to learning EDLIN is that it is always included with all PCs that use a release of DOS prior to Version 5.
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
If you use a computer other than a PC, such as a UNIX-based minicomputer or a mainframe, you have to determine which editors are available. Most UNIX systems include the vi editor. If you program on a UNIX operating system, it would be worth your time to learn vi . It is to UNIX what EDLIN is to PC operating systems, and is available on almost every UNIX computer in the world.
Mainframe users have other editors available, such as the ISPF editor. You might have to check with your systems department to find an editor accessible from your account.

Using a C++ Compile r
After you type and edit your C++ program’s source code, you have to compile the program. The process you use to compile your program depends on the version of C++ and the computer you are using. Borland C++ and Microsoft C/ C++ users need only press Alt- R to compile and run their programs. When you compile programs on most PCs, your compiler eventually produces an executable file with a name beginning with the same name as the source code, but ends with an .EXE file extension. For example, if your source program is named GRADEAVG.CPP, the PC would produce a compiled file called GRADEAVG.EXE, which you could execute at the DOS prompt by typing the name gr adeavg .
EXAMPLE

UNIX users might have to use the cf r ont compiler. Most cf r ont compilers actually convert C++ code into regular C code. The C code is then compiled by the system’s C compiler. This produces an executable file whose name (by default) is A.OUT. You can then run the A.OUT file from the UNIX prompt. Mainframe users generally have company-standard procedures for compiling C++ source pro- grams and storing their results in a test account.
 Unlike
many other programming languages, your C++ pro- gram must be routed
through a preprocessor before it is compiled. The preprocessor reads
preprocessor directives that you enter in the program to control the
program’s compilation. Your C++ compiler automatically performs the
preprocessor step, so it requires no additional effort or commands to
learn on your part.
Unlike
many other programming languages, your C++ pro- gram must be routed
through a preprocessor before it is compiled. The preprocessor reads
preprocessor directives that you enter in the program to control the
program’s compilation. Your C++ compiler automatically performs the
preprocessor step, so it requires no additional effort or commands to
learn on your part.
You might have to refer to your compiler’s reference manuals or to your company’s system personnel to learn how to compile programs for your programming environment. Again, learning the programming environment is not as critical as learning the C++ language. The compiler is just a way to transform your program from a source code file to an executable file.
Your program must go through one additional stage after compiling and before running. It is called the linking, or the link editing stage. When your program is linked, a program called the linker supplies needed runtime information to the compiled pro- gram. You can also combine several compiled programs into one executable program by linking them. Most of the time, however,
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
your compiler initiates the link editing stage (this is especially true with integrated compilers such as Borland C++ and Microsoft C/ C++) and you do not have to worry about the process.
Figure 2.2 shows the steps that your C++ compiler and link editor perform to produce an executable program.
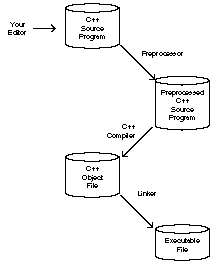
Figure 2.2. Compiling C++ source code into an executable program.
Running a Sample Progra m
Before delving into the specifics of the C++ language, you should take a few moments to become familiar with your editor and C++ compiler. Starting with the next chapter, “Your First C++ Program,” you should put all your concentration into the C++ programming language and not worry about using a specific editor or compiling environment.
EXAMPLE
Therefore, start your editor of choice and type Listing 2.1, which follows, into your computer. Be as accurate as possible—a single typing mistake could cause the C++ compiler to generate a series of errors. You do not have to understand the program’s content at this point; the goal is to give you practice in using your editor and compiler.
 Listing 2.1. Practicing with the editor.
Listing 2.1. Practicing with the editor.
Comment the program with the program name.
Include the header file iostream.h so the output properly works. Start of the mai n() function.
 Define
the BELL constant, which is the computer’s beep. Initialize the
integer variable ct r to 0.
Define
the BELL constant, which is the computer’s beep. Initialize the
integer variable ct r to 0.
Define the character array f name to hold 20 elements. Print to the screen What i s your f i r st name? .
Accept a string from the keyboard.
Process a loop while the variable ct r is less than five. Print the string accepted from the keyboard. Increment the variable ct r by 1.
Print to the screen the character code that sounds the beep. Return to the operating system.
/ / Fil ename: C2FI RST. CPP
/ / Request s a name, pr i nt s t he name f i ve t i mes, and r i ngs a bell . #i ncl ude <i ost r eam. h>
mai n( )
{
const char BELL=’ \ a’ ; / / Const ant t hat r i ngs t he bell i nt ct r =0; / / I nt eger var i abl e t o count t hr ough l oop char f name[ 20] ; / / Def i ne char act er arr ay t o hol d name
cout << “ What i s your f i r st name? “ ; / / Pr ompt t he user ci n >> f name; / / Get t he name f r om t he keyboar d
whil e ( ct r < 5) / / Loop t o pr i nt t he name
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
{ / / exact l y f i ve t i mes.
cout << f name << “ \ n” ; ct r ++;
}
cout << BELL; / / Ri ng t he t ermi nal’ s bell r et ur n 0;
}
Be as accurate as possible. In most programming languages— and especially in C++—the characters you type into a program must be very accurate. In this sample C++ program, for instance, you see parentheses, () , brackets, [] , and braces, {} , but you cannot use them interchangeably.
The comments (words following the two slashes, // ) to the right of some lines do not have to end in the same place that you see in the listing. They can be as long or short as you need them to be. However, you should familiarize yourself with your editor and learn to space characters accurately so you can type this program exactly as shown.
Compile the program and execute it. Granted, the first time you do this you might have to check your reference manuals or contact someone who already knows your C++ compiler. Do not worry about damaging your computer: Nothing you do from the keyboard can harm the physical computer. The worst thing you can do at this point is erase portions of your compiler software or change the compiler’s options—all of which can be easily corrected by reload- ing the compiler from its original source. (It is only remotely likely that you would do anything like this, even if you are a beginner.)
Handling Error s
Because you are typing instructions for a machine, you must be very accurate. If you misspell a word, leave out a quotation mark, or make another mistake, your C++ compiler informs you with an error message. In Borland C++ and Microsoft C/ C++, the error probably appears in a separate window, as shown in Figure 2.3. The most common error is a syntax error, and this usually implies a misspelled word.
EXAMPLE
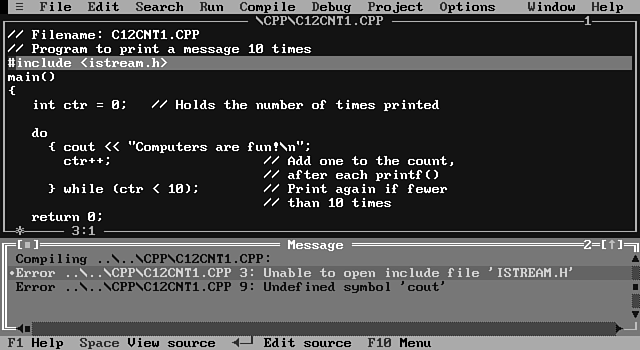
 Figure
2.3. The compiler reporting a program error.
Figure
2.3. The compiler reporting a program error.
When you get an error message (or more than one), you must return to the program editor and correct the error. If you don’t understand the error, you might have to check your reference manual or scour your program’s source code until you find the offending code line.
Chapter 2 ♦ What Is a Program?
After you have typed your program correctly using the editor (and you get no compile errors), the program should run properly by asking for your first name, then printing it on-screen five times. After it prints your name for the fifth time, you hear the computer’s bell ring.
This example helps to illustrate the difference between a pro- gram and its output. You must type the program (or load one from disk), then run the program to see its output.
Review Question s
The answers to the review questions are in Appendix B, “Answers to Review Questions.”
-
 What
Whatis a program?
-
What are the two ways to obtain a program that does what you want?
-
True or false: Computers can think.
-
What is the difference between a program and its output?
-
What do you use for typing C++ programs into the computer?
EXAMPLE
-
 What
Whatfilename extension do all C++ programs have?
-
Why is typing the program one of the last steps in the pro-
gramming process?
-
 What
Whatdoes the term debug mean?
-
Why is it important to write programs that are compatible with the
AT&T C++?
-
True or false: You must link a program before compiling it.
Summary
 After
reading this chapter, you should understand the steps necessary to
write a C++ program. You know that planning makes writing the program
much easier, and that your program’s instruc- tions produce the output
only after you run the program.
After
reading this chapter, you should understand the steps necessary to
write a C++ program. You know that planning makes writing the program
much easier, and that your program’s instruc- tions produce the output
only after you run the program.
You also learned how to use your program editor and compiler. Some program editors are as powerful as word processors. Now that you know how to run C++ programs, it is time to start learning the C++ programming language.

Your First C+ + Program
 This chapter
introduces you to some important C++ language commands and other
elements. Before looking at the language more specifically, many
people like to “walk through” a few simple programs to get an overall
feel for what a C++ program involves. This is done here. The rest of
the book covers these commands and elements more formally.
This chapter
introduces you to some important C++ language commands and other
elements. Before looking at the language more specifically, many
people like to “walk through” a few simple programs to get an overall
feel for what a C++ program involves. This is done here. The rest of
the book covers these commands and elements more formally.
This chapter introduces the following topics:
-
An overview of C++ programs and their structure
-
Variables and literals
-
Simple math operators
-
Screen output format
This chapter introduces a few general tools you need to become familiar with the C++ programming language. The rest of the book concentrates on more specific areas of the actual language.
Chapter 3 ♦Your First C++ Program
